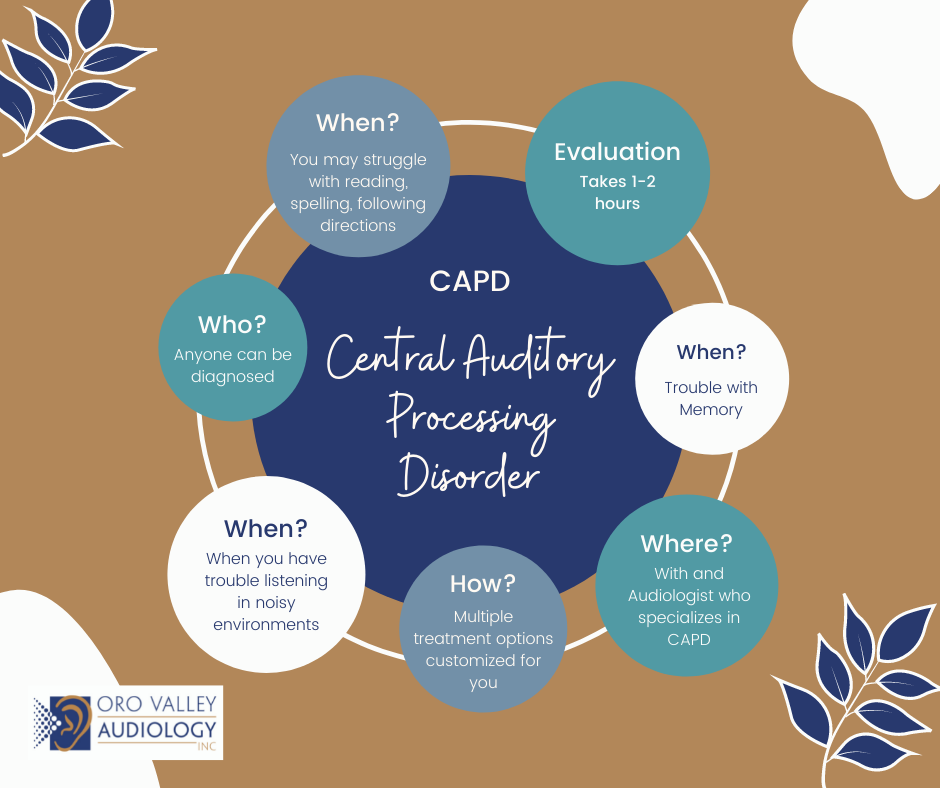
Who can diagnose a Central Auditory Processing Disorder?
Only an Audiologist can evaluate and diagnose a Central Auditory Processing Disorder. Processing is a complex task; those with auditory processing concerns may be referred to other specialties for further evaluation.
Who can be diagnosed with a Central Auditory Processing Disorder?
Any person of any age can be diagnosed with Central Auditory Processing Disorder.
What does a Central Auditory Processing Evaluation consist of?
The first step is to receive a comprehensive hearing test to determine hearing sensitivity as your audiologist will want to evaluate if your concerns are related to a potential hearing loss. If your hearing thresholds are within the normal to near-normal range, you may be referred for a Central Auditory Processing Evaluation. A Central Auditory Processing evaluation consists of a series of tests that include listening to a variety of signals including speech and tones. The variety of tests evaluates various areas in the brain where auditory processing occurs. The evaluation typically lasts for 1-2 hours for which breaks can be given as needed. The goal of the Central Auditory Processing evaluation is to determine if there are processing deficits and the nature of these differences. Knowing the type of auditory deficit allows for individualized management and to target specific needs.
Where can a Central Auditory Processing Evaluation be completed?
Central Auditory Processing Evaluation will be completed by an Audiologist who specializes in Central Auditory Processing Disorder (CAPD). These types of appointments can be completed at any clinic or office that provides these services. Should your local clinic not provide CAPD services, an appropriate recommendation to another audiologist will be made.
When should you consider a CAPD evaluation?
Those with auditory processing differences may experience uncertainty about what they hear and have difficulty listening in challenging situations such as classrooms or busy work environments. Those with processing deficits may also struggle with reading, spelling, and following directions. Other difficulties may include, sound localization, listening in the presence of background noise, inability to isolate or identify a sound source, poor auditory memory, and delayed responses. If you have any of these concerns, its best to schedule a comprehensive hearing test. Should results from this evaluation be within normal limits, the audiologist may recommend a CAPD evaluation.
How is CAPD treated?
Current intervention options include but are not limited to, auditory training, amplification, environmental modifications, and assisted listening devices. Intervention and recommendation options will be discussed in detail between you and your audiologist to determine the most appropriate action plan. There is no one sure-fire way to treat CAPD, intervention, and recommendations are individualized to meet your specific needs.